Introduction & Motivation
Entropy and Information: Concepts and applications
CMPLXSYS 445
Saturday, December 6, 2025
Outline
- About me
- About you
- Course overview
- Motivation
About me
- 5th Year PhD Candidate in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
- BS/MS In Biology and Physics, Indian Institute of Science
- Using information theory to understand how an organism can store information about its environment in the genetic code.
Research interests
- How do living systems (real or artificial) adapt to their environment in creative ways?
- Can we use theoretical tools to control evolution and engineer better biological systems?

About you
- Your name, program, and year
- Why learn information theory?
Course Overview
Website
- Course website: kumawatb.github.io/cmplxsys445_fa2025/ (Bookmark it! Also linked on Canvas homepage)
- Contains everything you would need:
- Syllabus
- Assignments
- Lecture notes/slides/readings
- Links to external tools: Canvas (announcements), Gradescope (assignments), Ed (Q & A)
Course Overview
Office Hours
- In-person: Monday 11:30AM-12:30PM (Weiser 730)
- Online: Wednesday 11:30AM-12:30PM (Zoom, see website for link)
- Email me to schedule another time for a meeting!
Course Overview
Assessment
- Assignments (50%)
- Midterm (20%)
- Date & Time: October 15, 10:00am to October 16, 10:00am
- Details: Take home, open book/notes/computational tool, no class on Wednesday Oct 15, upload on gradescope
- Final (20%)
- Date & Time: Dec 15, 4:00pm to 6:00pm
- Details: In-person, open book/notes
- Final Presentation (10%)
- Oral presentation (5-6 mins)
- Topic(s): You choose! (Some suggested topics on course website)
- Topic decision due date: Oct 10
- Recorded practice due date: Nov 11
Motivation
Why study entropy and information?
- Probability theory tells you the chances of an outcome
- Information theory tells you about the uncertainty of an outcome
- Eg. Weather
- 0% or 100% chance of rain (High certainty ~ Low entropy).
- 50% chance of rain (Low certainty ~ High entropy).
- Information based measures can tell us
- How much we know about something (something = random variable(s))
- What can we know for certain based on some partial information (Eg. MaxEnt)
- About limitations of physically bottlenecked systems, because of its close relation to thermodynamics (Eg. Why we can’t build an infinitely efficient computer)
Motivation
Entropy vs information
- Entropy: Quantifies how much we don’t know.
- Information (qualitative): That which allows us to make predictions with accuracy better than chance.
- Information (quantitative) = Reduction in entropy after we get some new information.1
Motivation
Information theory in: Statistics
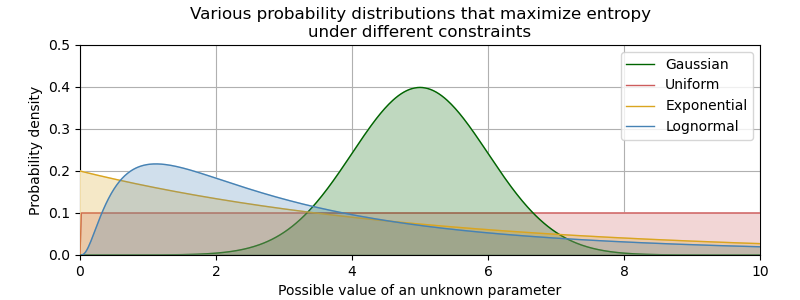
- Maximum Entropy: Maximize entropy given current constraints to best represent the state of knowledge about a system.
- Eg. If we know that an unknown probability distribution has a given mean and variance, the normal distribution with this mean and variance is the most entropic (and hence the most unbiased) distribution.
- Sufficient Statistics: What property of some data is sufficient to say something about its underlying distribution?
- Eg. For data generated from a normal distribution with a known variance, the sample mean of the data is sufficient for the mean of the underlying distribution (i.e., you can get no extra information by looking at the data that you cannot get from the sample mean about the real mean)
Motivation
Information theory in: Computer Science
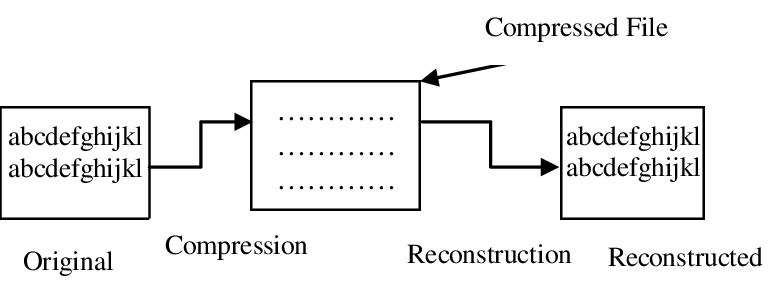
How much can you compress a file?
How much learning can a machine do?
Motivation
Information theory in: Finance
- Value of information: How should you distribute your money across investments to maximize long term gain? What’s the expected growth rate given a distribution? How does new information affect this?
Motivation
Information theory in: Linguistics
- Do faster spoken languages contain less information per syllable?1
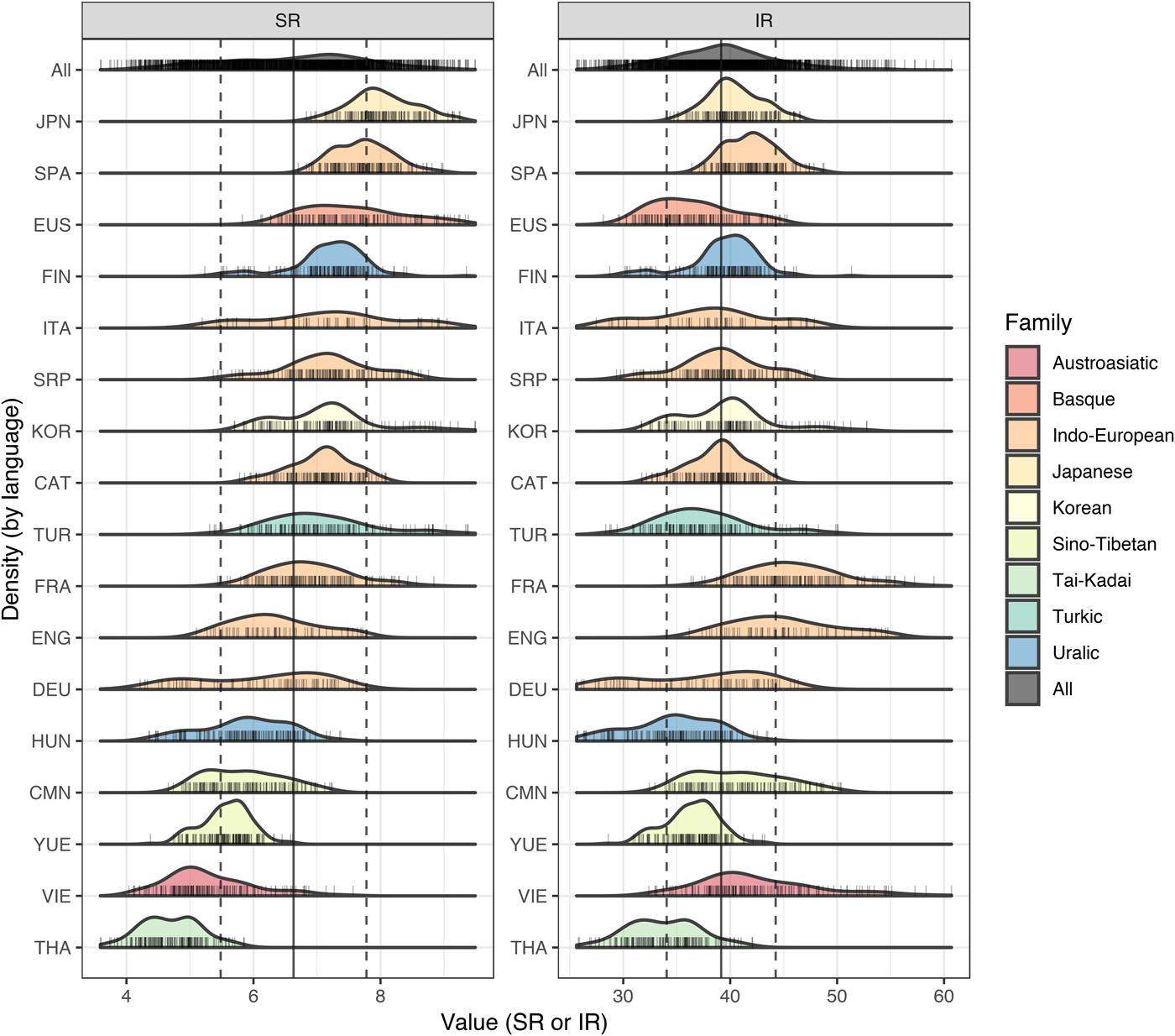
- How to optimally name colors in a language to allow maximal accuracy with minimal complexity?2
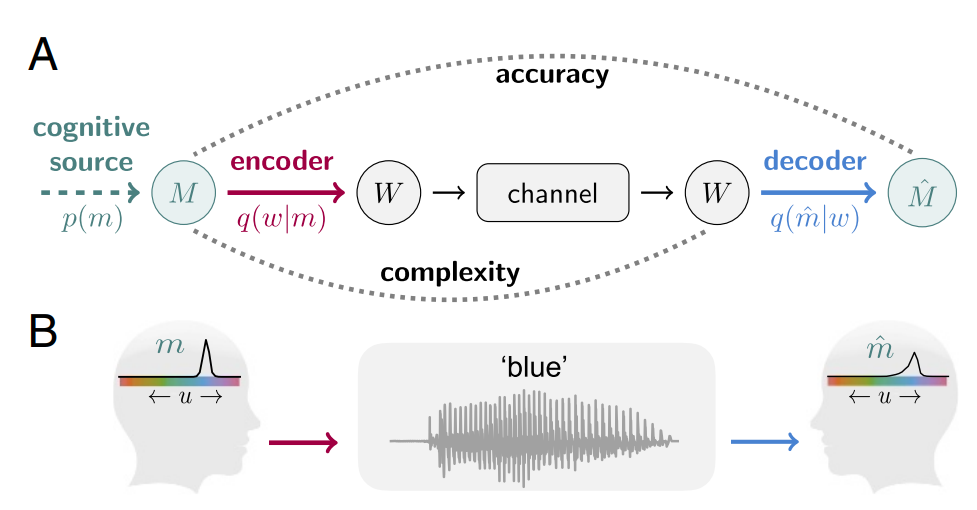
Motivation
Information theory in: Physics
- Thermodynamics of computation: How much computation can we get out of a single unit of energy? 1
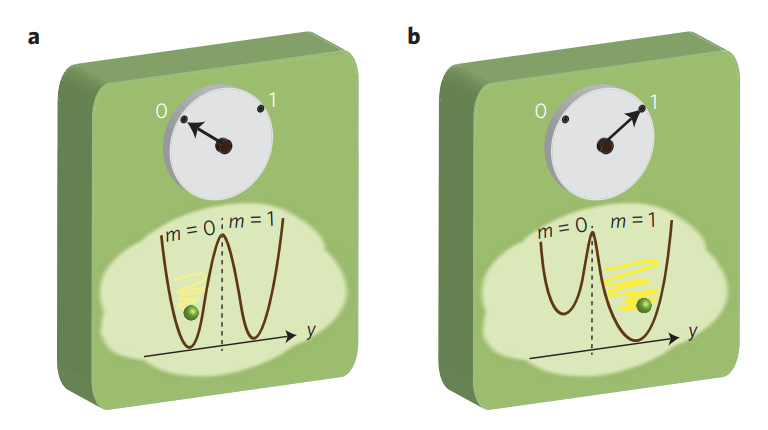
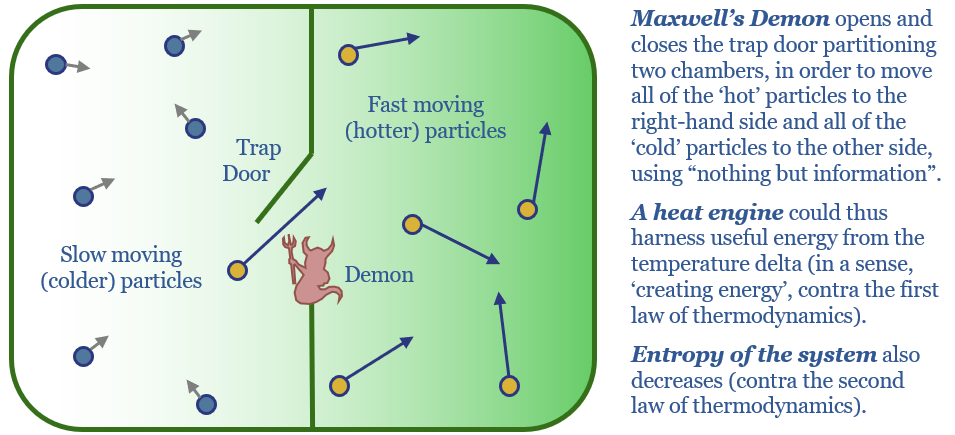
- Why does Maxwell’s demon not violate the second law?
Motivation
Information theory in: Biology
- What are the fundamental limits to the functioning of a biological system?
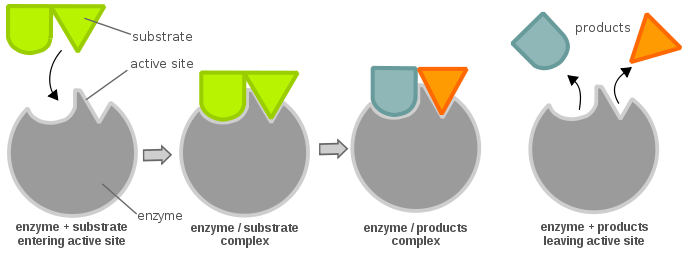
- Can evolving organisms store information about past environments to evolve better in the future?1
What’s next
Lecture
- Introduction to probability theory (boring but useful)
To-dos
- Check out the course website
- Login to Gradescope and Ed (Q&A site)
- Download scanner app on your phone, and try using it